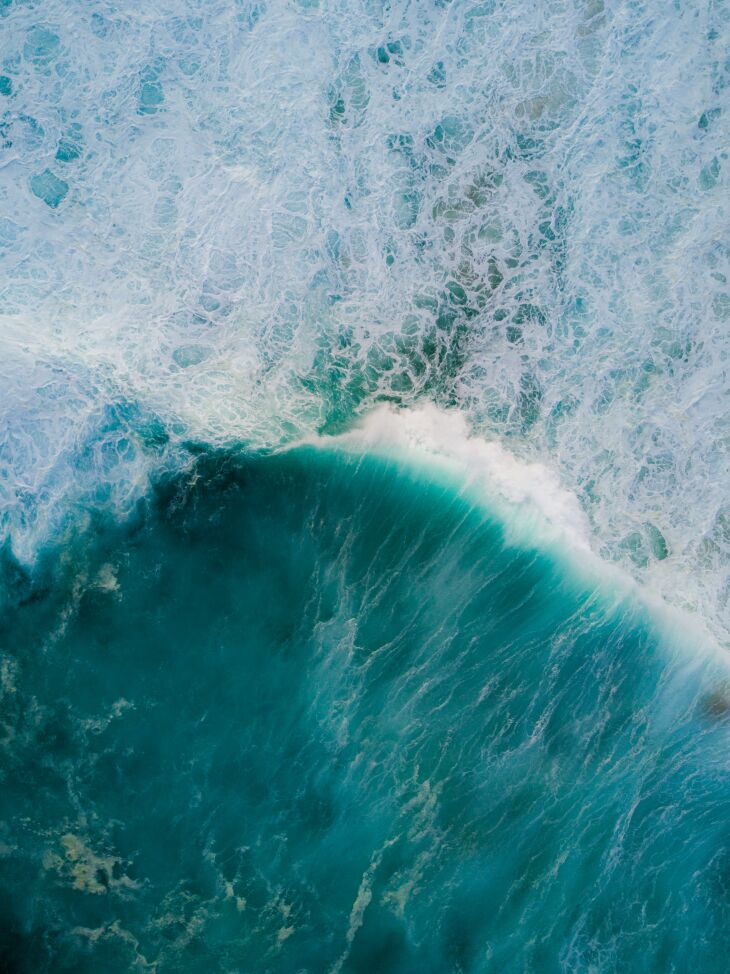
People tend to think of sharks as large, frightening predators with sharp teeth, so it might come as a surprise to learn that some shark babies grow in the same way as humans – attached to the mother by an umbilical cord and placenta.
Our recent research published in the Journal of Comparative Physiology B sheds light on the placenta of the pint-sized Australian sharpnose shark – wherein a thin layer of egg capsule separates the mother’s and baby’s tissues.
Shark pregnancy
There are more than 500 different species of shark, some as small as your hand (like the dwarf lantern shark) and others as big as a bus (such as whale sharks).
Reproduction in sharks is equally varied: some lay eggs, but most give birth to live young. Sharks typically give birth after 11–12 months of pregnancy, but some, such as the frilled shark, are pregnant for more than three years.
In some sharks, a placenta develops during pregnancy. The placenta helps the baby shark breathe, eat and expel waste as it develops inside the mother. Other species of shark don’t have a placenta, and instead their babies feed on egg yolk, secretions, unfertilised eggs or even their own siblings.
Biologists have long been fascinated by reproductive diversity in sharks, but haven’t yet figured out why some sharks have placentas and others don’t.
The Australian model for shark pregnancy
In Australia, we have a unique model to understand shark pregnancy: the Australian sharpnose shark (Rhizoprionodon taylori). This small shark is just 70 centimetres long, and lives off the coast of northern Australia.